Know Your Honey
Fraud honey is a global threat to beekeeping.
Fake honey is a well know fact – the EU states 50% is fraud and has identified 5 common methods, see below. The counterfeit affects beekeepers all over the world, large and small, and of course consumers.
The goal is to develop a new standard for authentic honey and Good Goods.
Funding is sought through the Swedish Board of Agriculture, European Innovation Program.

Image 1. Some “authentic” honey in a Swedish Supermarket.
Explosion in honey fraud
Honey is one of the most counterfeited foods in the world (note 1). Worth billions, it is easy to counterfeit but difficult to control. The value of honey globally is over SEK 90 billion in 2022 and is estimated to increase to SEK 260 billion in 2028 (note 18). Huge values are damaged for both consumers and producers by fraudulent handling of a unique raw material.
Internationally, the need to combat the counterfeiting of honey is a high priority. Between 30-70% of the honey on the world market is more or less adulterated (note 11). A coordinated EU action in May 2023 states that about 50% is counterfeit (notes 12-13). Another example is Asia: exports from East Asian countries have gone from 100 million tons in 2010 to 325 million tons in 2018. China exports twice as much ‘honey’ as it has bees for. Exports have tripled, but the number of colonies remains unchanged (Note 16).

Image 2. “Certified” Non-EU-farming, ecological honey?!
Analyses alone fails
Despite great efforts to develop analytical methods to detect adulteration, this has failed and has not prevented further cheating (note 14). On alibaba.com you can buy “honey” for €1,4/kg, with a few extra cents you can get labels such as organic or other certificates..
Image 3. Chinese “honey”?
The methods of transforming rice syrup with colors and flavors and even the addition of pollen are ahead of the analyses that can detect such cheating. Calls for stricter rules on origin labeling, increased controls and even import restrictions are becoming louder and more frequent. Unfortunately, this is more or less in vain as there yet are no tools to tackle this large-scale criminal fraud.
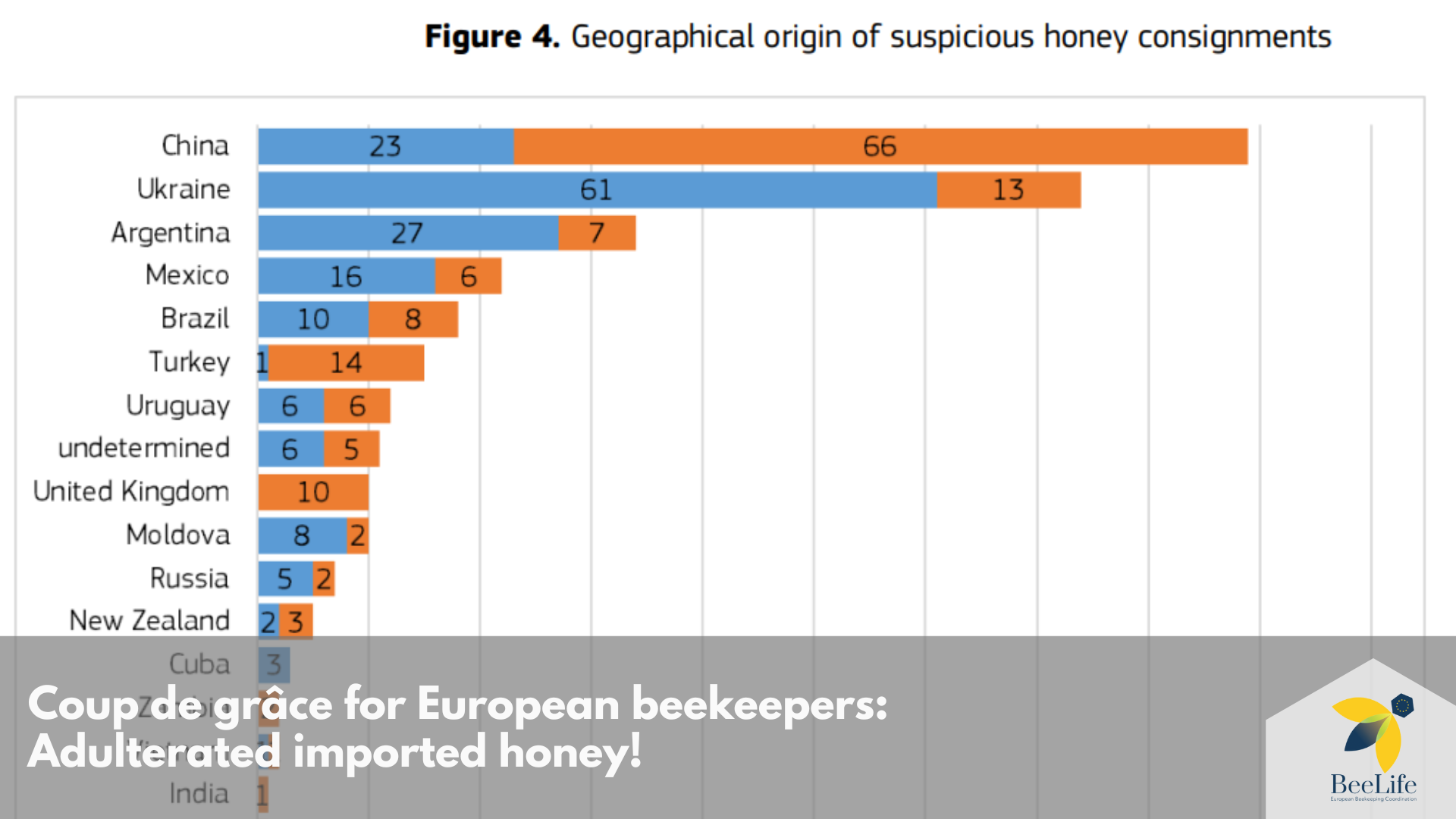
Image 4. EU investigation of geographical origin (BeeLife)
Souce of problem
1. The small hobby beekeepers are not really the problem. They have no reason to cheat; they are proud of their craft. You can usually trust their word that they are harvesting real honey. However, this is a matter of trust and there is no objective proof. Hobby beekeepers are affected by cheating indirectly through lower valuation of the honey and distrust from some consumers (note 19).
2. Larger beekeepers, with a few hundred colonies or more, may have an economic interest in improving their performance by illicit means, especially if they are under pressure from both cheap foreign mixed honey as well as counterfeit competition. However, this is likely to be marginal in Sweden and in some parts of the western world. Beekeepers and associations tend to keep a fairly good eye on their colleagues locally. However, in some countries, there is a fairly widespread perception that cheating is legion, and it is therefore considered that comb honey provides some guarantee of authenticity. But there is no objective documentation to prove either the origin or the authenticity of the honey.
3. The way the honey market operates, cheating occurs mainly at the packer and retail level. Retailers are happy to do good business buying at low prices as long as the supplier can show the right certificate. Bottlers are satisfied with being able to buy for €1,5/kg, mix with real honey or sell directly to the trade for €10/kg. The consumer pays €15/kg. No objective evidence can be presented.

Image 5. Labeled frameless super with combhoney from FriBi HB
Solution structure


Solution
-
ID-labeling supers
-
App collects manual and automatic data
-
AI – analysing images
-
Analyses of honey
-
Blockchain technology.
1 ID-labeling supers
The project offers a unique solution based on verifying the raw commodity at the time of harvest with AI analysis of images of the harvest before it ends up in a container. In the case of honey, it needs to be linked to harvesting from a specific bee colony in an identified hive in a precise location (see Figures 5 and 6, labeling honey supers). Beekeeping in the world has so far lacked possibilities for objective identification of frames and boxes. This is related to past difficulties in documenting, verifying and recording labeled units. The labeling itself can be made very simple without costs.
2 App collects manual and automatic data
There are two kinds of data collected, supporting each other. Preliminary data that the user generates setting up account and the content of the business, editing management tasks through the season , adding supers, changing queens, harvesting. Secondary data are built from external sources like meteorology, land use, crops grown, statistics from regional historical data about beehive density, normal harvesting patterns, yield per colony.
3 AI- analysing images
If a characteristic can be seen in an image then AI can be trained to register and assess it. A beekeeper can tell if the honey is ready to harvest and estimate how much a honey super weighs from only looking at it. This is the basis for using AI to objectively document the preliminary data entered harvesting.
4 Analyses of honey
Validation of the authenticity and origin of honey is thus not based solely on analyses of honey, but the analyses can constitute so-called proof points in a chain of transactions. The project will determine which analyses will be integrated, and the possibility of authorizing analysis providers, in order to maintain the quality of the input data in the system. The analyses can constitute “fingerprints” for validation and include: pollen content, chemical analyses of sugars, fragrances, other substances such as environmental toxins, pesticide residues, microbiological analyses of harmful and beneficial microbes, and last but not least DNA analyses to map the honeybee’s macro and micro environment, and possibly images from MRI analyses.
5 Blockchain technology
The entire chain is secured and validated via blockchain technology. With secured data, the honey industry can demand the individual steps of a complete solution. Furthermore, this can give the beekeeper constructive feedback on the quality of his honey and what measures may need to be taken to improve the quality of the production.
Blockchain will also provide new and more efficient logistic, administration and so called smart contracts.
The system is a unique approach that can serve as a model in the world for honey and other raw materials.
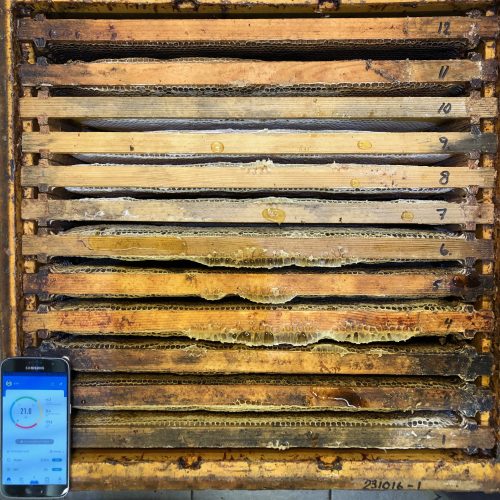

Image 6. Weighed and labeled super.

Image 7. Editing hives

Image 6. Training AI

Image 7. Close-up of a honey sample at 4500 x magnification. The image shows pollen, various microbes and other substances. There is a diversity of organisms and substances that we do not know much about. Modern methods that detect both microbes and DNA can help characterize a honey sample in much more detail than classical chemical methods can do. Image taken at the Umeå Center for Electron Microscopy by Natuschka Lee.

Image 8. An analogy in beekeeping could be the division of a bee colony. The legacy is passed on to the new queen. This cannot be removed. However, new information, i.e. male DNA, is added during mating that will be present and passed on to the next generation ….
Fraudulent practices
As defined by the EU
1. Use of sugar syrup (from rice or corn) to adulterate honey and reduce its price, both in non-EU countries and on EU territory.
Revealed by: The quantity cannot be linked to a defined origin. Missing, inaccurate, discrepant producer data, hive ID data, treasure box, GPS image evidence, time of harvest and AI analysis of harvest image. Missing data from extraction. Missing secondary data on crops and harvest in the region, missing reference sample.
2. Analysis in accredited laboratories to adjust mixtures of honey and sugar to avoid detection by customers and official authorities before import.
Revealed according to 1 above complemented by DNA, pollen, microbes and NMR analysis with reference library.
3. Use of additives and colorants to falsify the true botanical source of the honey.
Revealed according to 1 and 2 above.
4. Masking the true geographical origin of the honey by falsifying traceability information and by removing pollen, or adding foreign pollen.
Disclosed by blockchains securing the data under 1 and 2.
5. Feeding of bee colonies with sugar during nectar flow
Revealed by wrong sugars and their relationship. Wrong pollen content. Revealed by unreasonableness of harvest in relation to secondary data such as available nectar sources, comparable data regional production, comparable data history. Revealed by audit of financial accounts.

Image 9. Only sophisticated combination of methods can combat the complex fraud operations.
The End Product
The product is an activated QR code on the packaging that allows the consumer to scan and verify the origin and authenticity. This connects the customer with the producer’s information from the different stages of production. The producer can choose how deep the customer can look into all the details of the production.
Value:
The beekeeper and honey extractor can be better paid if they can gain the customer’s trust that the product is genuine and the cheapest fraudulent products are limited.
Voluntary:
The system will be voluntary to use. When consumers value the ability to see the origin of the product, demand is created.
Competition:
For the producer, the beekeeper, traceability becomes a competitive tool against those who cannot provide objective traceability.

Image 10. Scan QR
Economy
Potential Economic Value Added Through Price Premiums (note 9)
Table 1: Value of origin (source De Pelsmacker et al 2005, National Honey Board 2019, European Commission 2017, Deselnicu et al 2013, from left to right).
| Impact of | Fair Trade | Organic bulk | Varietals | Local origin |
| Price premiums | 10-27% | 7 % | 27 % | 21 % |
We envisage a model based on a fixed and a variable component. The fixed part consists of an annual subscription and varies with the number of hives. The variable part varies between 0.5 – 5% of the product value. The impact of traceability on the value of the honey can be set at an increase in value of 10 – 30% at each stage of the transactions.
The Regulatory Framework
“The Breakfast Directive”

Proposal for a DIRECTIVE OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL amending Council Directives 2001/110/EC relating to honey, ... Brussels, 12 February 2024.
(9). In order to protect consumers’ interest and to limit as much as possible fraud linked to adulterated products that do not correspond to the designation of ‘honey’, to enable the validation of information provided about the honey’s origin and quality, and to provide utmost transparency, the Commission should adopt delegated acts to introduce traceability requirements that ensure the availability of and access to essential information concerning the origin of the honey, including country of origin along the EU supply chain, from harvesting producer or importer to consumers. Therefore, harmonised traceability requirements for honeys produced and imported into the Union are necessary to enable the competent authorities of Member States to be able to trace the entire chain at least back to the first step within EU borders. Those rules should not add to the administrative burden of producers but should make it easier for consumers and the supervisory authorities to keep track of the honey’s entire journey from harvesting to bottling in the Union. Therefore, through the new honey traceability requirements, honey origin and authenticity along the honey value chain should be ensured. With a view to a traceability system, and in order to elaborate the most appropriate requirements, including analysis of available digital solutions or methods, including where appropriate, a unique identifier code or similar techniques, the Commission should carry out a feasibility study.
(10). In order to support the Commission with the best available technical expertise, a platform should be established. The Platform should, inter alia, provide recommendations for a Union traceability system that ensures the availability of and access to essential information on the origin of the honey or honey in a blend, including where appropriate the country of origin, the year of production and a unique producer identifier, along the EU supply chain, from the harvesting producer or importer to the consumer. It should also support the future establishment of an EU reference laboratory for honey to improve controls and detect adulteration in honey through harmonised methods, systematic testing of honey using the latest testing methods to prove the authenticity and quality of honey as laid down in the Directive.
Participation
We have an outstanding setup of international partners. We seek collaboration with beekeepers who can provide honey supers for photography or images of these for training the AI as well as testers to suggest ways to prevent practices that try to circumvent the system. We also look for representatives of the traders and retail to join.
Partners
Notes
1. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-32764-w
2. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/honey-market-100551
3. https://www.cropin.com/blogs/following-the-hive-to-honey-trail-using-digital-traceability
4. https://www.sourcetrace.com/blog/tackling-honey-traceability/
5. https://www.nsf.org/testing/food/food-beverage-product-certification/honey-traceability
6. https://truesourcehoney.com/faqs/#24984da1-1054-49b5-a01a-0adebc379e77
7 https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2022/11/21/2560047/0/en/Global-Honey-Market-Revenue-to-Reach-25-8-Billion-1-8-Million-Metric-Tons-of-Honey-is-Produced-India-and-China-are-the-Largest-Producer-of-Honey.html
9. https://jisar.org/2022-15/n1/JIARv15n1p24.pdf sid 24-30
10. https://www.fao.org/3/cb5353en/cb5353en.pdf sid 146
11. https://www.vice.com/en/article/884kq4/your-fancy-honey-might-not-actually-be-honey
12. https://www.foodwatch.org/en/half-of-eus-imported-honey-supply-suspected-to-be-fake
13. https://food.ec.europa.eu/safety/eu-agri-food-fraud-network/eu-coordinated-actions/honey-2021-2022_en
14. https://www.wired.co.uk/article/honey-fraud-detection
15. https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2011/08/honey-laundering/?utm_source=American+Bee+Journal&utm_campaign=f758f051b5-American_Bee_Journal_Newsletter_6_15_2011&utm_medium=email
16. https://www.apiservices.biz/documents/articles-en/history_honey_fraud.pdf
17. https://cnhoney.en.alibaba.com/index.html?spm=a2700.shop_pl.88.12
18. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/honey-market
19. Land Lantbruk nr 35 25 augusti 2023, sid 6-10.
20. https://www.axfoundation.se/projekt/samverkan-kring-blockkedjan-i-livsmedelskedjan
Image sources:
All images BeeScanning except #2 (note 17) and #6 Natuschka Lee.













